Beginning with Risk-based asset allocation strategies, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
Asset allocation is a critical aspect of investment strategy, and understanding risk-based approaches can lead to more informed decisions with potentially higher returns. This article delves into the intricacies of risk-based asset allocation strategies and their impact on portfolio management.
Risk-based Asset Allocation Strategies

Risk-based asset allocation strategies refer to investment approaches that take into consideration various risk factors when deciding how to allocate assets within a portfolio. These strategies aim to optimize risk-adjusted returns by balancing the level of risk exposure with potential returns.
Incorporating risk factors into asset allocation decisions is crucial because it helps investors manage and mitigate potential losses. By diversifying across different asset classes based on their risk profiles, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolios while still aiming for attractive returns.
Comparison with Traditional Asset Allocation
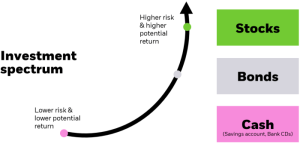
Compared to traditional asset allocation methods that primarily focus on asset class diversification without considering risk factors, risk-based asset allocation strategies offer a more nuanced approach. Instead of simply spreading investments across stocks, bonds, and cash, risk-based strategies take into account factors like volatility, correlation, and downside risk.
Examples of Risk-based Asset Allocation Strategies
- Minimum Variance Portfolio: This strategy aims to construct a portfolio with the lowest possible volatility, considering the covariance matrix of asset returns. By minimizing risk, investors seek to achieve stable returns even in turbulent market conditions.
- Risk Parity: In a risk parity strategy, assets are allocated based on their risk contribution to the overall portfolio, rather than their market value. This approach aims to balance risk exposure across different asset classes, diversifying risk more effectively.
- Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR): CVaR is a risk measure that considers the potential losses beyond a certain confidence level. By incorporating CVaR into asset allocation decisions, investors can better manage extreme downside risk and protect their portfolios during market downturns.
Asset Management

Asset management refers to the strategic management of a variety of investments and assets to achieve specific financial goals. Key components of asset management include portfolio construction, asset allocation, risk management, and performance evaluation.Asset management plays a crucial role in optimizing portfolio performance by ensuring that investments are aligned with an individual’s or institution’s risk tolerance, investment objectives, and time horizon.
By diversifying investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions, asset managers aim to minimize risk while maximizing returns.The strategies employed in asset management can vary based on an individual’s or institution’s risk appetite and investment goals. For example, a conservative investor may opt for a more defensive asset allocation strategy, focusing on lower-risk investments such as bonds and cash equivalents.
On the other hand, an aggressive investor with a higher risk tolerance may pursue a more growth-oriented strategy, investing in equities and alternative assets.Financial institutions use a range of asset management techniques to help clients achieve their financial objectives. These techniques may include active portfolio management, passive index investing, tactical asset allocation, and dynamic risk management. By leveraging these strategies, asset managers seek to generate consistent returns while managing risk effectively.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the strategic distribution of investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents within a portfolio. It plays a crucial role in portfolio diversification by spreading risk and maximizing returns.Strategic asset allocation involves setting target allocations for different asset classes based on an investor’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. By maintaining a diversified portfolio, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility and achieve long-term investment growth.
Benefits of Strategic Asset Allocation
- Minimizes Risk: By spreading investments across different asset classes, strategic asset allocation helps reduce the overall risk in a portfolio.
- Maximizes Returns: Optimal allocation of assets based on risk and return expectations allows investors to achieve the highest possible returns given their risk tolerance.
- Long-Term Growth: A well-structured asset allocation strategy can provide consistent growth over the long term, helping investors meet their financial objectives.
Impact of Asset Allocation on Risk Mitigation and ROI
Asset allocation is the primary determinant of a portfolio’s risk and return characteristics.
By adjusting the allocation of assets in a portfolio, investors can manage risk exposure and optimize returns. For example, a conservative investor may choose to allocate a higher percentage of assets to fixed-income securities to minimize risk, while an aggressive investor may lean towards equities for higher growth potential.
Examples of Asset Allocation Models
| Risk Profile | Asset Allocation |
|---|---|
| Conservative | 60% bonds, 30% stocks, 10% cash equivalents |
| Moderate | 40% bonds, 50% stocks, 10% cash equivalents |
| Aggressive | 20% bonds, 70% stocks, 10% cash equivalents |
In conclusion, risk-based asset allocation strategies offer investors a dynamic approach to portfolio management, balancing risk and return in a strategic manner. By incorporating risk factors into asset allocation decisions, investors can tailor their strategies to meet their financial goals effectively.
Clarifying Questions
How do risk-based asset allocation strategies differ from traditional methods?
Risk-based asset allocation strategies focus on incorporating risk factors into investment decisions, while traditional methods may rely more on historical data and fixed allocations.
What are some examples of risk-based asset allocation strategies used in different market conditions?
Examples include dynamic asset allocation, risk parity strategies, and factor-based asset allocation models, each tailored to specific market environments.
How does asset management play a role in optimizing portfolio performance?
Asset management involves overseeing investments, making strategic decisions, and rebalancing portfolios to achieve optimal performance levels based on risk tolerance and investment objectives.