With Dynamic asset allocation approach at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Dynamic asset allocation involves a strategic approach to optimizing investment returns by adjusting asset allocations dynamically based on market conditions. This method contrasts with static asset allocation, offering flexibility and potential for higher returns. Throughout this discussion, we will delve into the concept, benefits, and real-world applications of this dynamic strategy.
Dynamic asset allocation approach

Dynamic asset allocation is an investment strategy where the allocation of assets in a portfolio is adjusted based on changing market conditions and economic outlook. This approach aims to maximize returns while minimizing risk by actively managing the asset mix.
Examples of dynamic vs. static asset allocation
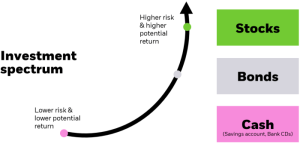
- In static asset allocation, the percentages of assets in a portfolio are fixed and do not change over time. For example, a portfolio might have 60% stocks and 40% bonds regardless of market conditions.
- On the other hand, in dynamic asset allocation, the percentages of assets are adjusted periodically based on market trends, economic indicators, and other factors. For instance, if the stock market is expected to perform well, the allocation to stocks may increase.
Benefits of using a dynamic asset allocation approach
- Flexibility: Dynamic asset allocation allows investors to adapt to changing market conditions and take advantage of opportunities as they arise.
- Risk management: By actively adjusting the asset mix, investors can better manage risk and reduce the impact of market downturns.
- Potential for higher returns: With a dynamic approach, investors have the potential to capture gains in different market environments and optimize their returns.
Real-world scenarios of effective dynamic asset allocation
One real-world scenario where dynamic asset allocation has proven effective is during periods of economic uncertainty. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, investors who dynamically adjusted their asset allocation to reduce exposure to risky assets were able to limit losses and preserve capital. Another scenario is in times of market volatility, where dynamic asset allocation can help investors navigate turbulent market conditions and capitalize on opportunities for growth.
Asset Management

Asset management is a crucial aspect of financial planning that involves the management of investments to achieve specific financial goals. It plays a vital role in helping individuals and organizations make informed decisions about their investments to maximize returns while minimizing risks.
Key Components of Asset Management
- Risk Assessment: Asset managers assess the level of risk associated with different investment options to make informed decisions.
- Portfolio Diversification: Asset managers diversify investments across various asset classes to reduce risk exposure.
- Performance Analysis: Asset managers regularly analyze the performance of investments to track progress towards financial goals.
Role of Asset Management
- Maximizing Returns: Asset management aims to generate maximum returns on investments by strategically allocating assets.
- Minimizing Risks: Asset management helps in minimizing risks by diversifying the investment portfolio and implementing risk management strategies.
Strategies Used in Asset Management
- Passive Management: Involves investing in a diversified portfolio that mirrors a market index to achieve average market returns.
- Active Management: Involves actively buying and selling investments to outperform the market and generate higher returns.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is a crucial strategy in portfolio management that involves dividing investments among different asset classes to achieve diversification and manage risk effectively.
Examples of Asset Classes
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with higher volatility.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing regular income and lower risk compared to stocks.
- Real Estate: Investments in physical properties, offering potential for appreciation and rental income.
Importance of Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation plays a key role in achieving long-term investment goals by aligning the portfolio with the investor’s risk tolerance and objectives. It helps in maintaining a balanced mix of assets based on their expected returns and correlations.
Comparison of Asset Allocation Models
There are different asset allocation models, each with its unique approach:
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions or economic outlook.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: Focuses on adjusting the asset mix dynamically in response to changing market conditions and investment opportunities.
In conclusion, Dynamic asset allocation approach provides investors with a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of financial markets effectively. By adapting allocations in response to changing market dynamics, investors can enhance returns and manage risks more efficiently. Embracing this approach opens up a world of possibilities for achieving long-term financial goals with confidence and agility.
Q&A
What is dynamic asset allocation?
Dynamic asset allocation involves adjusting the allocation of assets in a portfolio based on changing market conditions to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
How does dynamic asset allocation differ from static asset allocation?
Dynamic asset allocation involves actively adjusting asset allocations based on market conditions, while static asset allocation maintains a fixed allocation regardless of market changes.
What are the benefits of using a dynamic asset allocation approach?
Dynamic asset allocation offers flexibility to adapt to market fluctuations, potentially leading to higher returns and better risk management compared to static allocation strategies.
Can you provide real-world examples of dynamic asset allocation in action?
One example is during market downturns, where investors may increase exposure to defensive assets to protect their portfolios. Another scenario is when economic indicators point to growth, prompting a shift towards riskier assets for higher returns.